Coffee is one of the most widely consumed beverages globally, with millions of people relying on it as their daily cuppa. However, the coffee industry has a significant impact on our planet’s future if certain changes are not made to current practices. As the world’s population continues to grow, so does the demand for coffee, putting pressure on farmers to produce more while maintaining quality. But at what cost? The environmental and social implications of the lack of sustainable coffee farming practices are alarming, from deforestation and water scarcity to pesticide use and climate change.
Coffee farming can have a significant impact on our planet’s future if certain changes are made in current practices. Let’s explore the challenges faced by the coffee industry, including the effects of climate change, pest infestation, soil degradation, and water scarcity, as well as potential solutions for sustainable coffee farming practices
Challenges Faced by the Coffee Industry
Climate Change and its Effect on Crop Production
Climate change is one of the most significant challenges faced by the coffee industry. Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns affect coffee yields, quality, and even the very existence of certain coffee-growing regions.
Warmer temperatures can lead to an increase in pests and diseases, while droughts can devastate entire harvests. The consequences are far-reaching, with coffee prices rising due to decreased yields and increased demand for sustainable products.
Pest Infestation Leading to Decreased Yields and Quality of Beans
Pest infestations are a major issue in the coffee industry. Coffee berry borer (Hypothenemus hampei) is one of the most destructive pests, causing widespread damage to crops. The use of pesticides can exacerbate the problem, leading to decreased yields and lower-quality beans.
Organic farming practices, such as integrated pest management (IPM), offer a more sustainable solution.
Soil Degradation Due to Monoculture Farming Techniques
Monoculture farming techniques, where a single crop is grown on a large scale, have led to soil degradation in many coffee-growing regions. This can result in reduced fertility, increased erosion, and decreased water retention capacity.
Diversifying crops grown alongside coffee plants can help maintain soil health.
Water Scarcity Issues Related to Growing Coffee Crops
Coffee production requires significant amounts of water, particularly during the growing season. Water scarcity is a growing concern, especially in regions where water resources are already limited. Sustainable farming practices that conserve water and reduce waste can help alleviate this issue.
Solutions for Sustainable Coffee Farming Practices
Organic Farming Techniques That Reduce Chemical Runoff into Water Sources
Organic farming practices can significantly reduce chemical runoff into water sources, improving overall environmental sustainability.
By avoiding synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, farmers can minimize their impact on local ecosystems and waterways.
This approach not only benefits the environment but also produces higher-quality coffee beans with unique flavor profiles.
Diversifying Crops Grown Alongside Coffee Plants for Added Soil Nutrition
Diversifying crops grown alongside coffee plants is a simple yet effective way to promote soil health and biodiversity. By incorporating legumes, herbs, or other nitrogen-fixing crops, farmers can replenish the soil’s nutrients, reduce erosion, and create habitats for beneficial insects and microorganisms.
Utilizing Shade-Grown Methods That Promote Biodiversity Preservation
Shade-grown coffee farming is a sustainable approach that mimics nature’s canopy layer. By growing coffee plants under a shaded environment, farmers can reduce their reliance on pesticides, promote biodiversity, and conserve water.
This method also results in higher-quality beans with more complex flavor profiles.
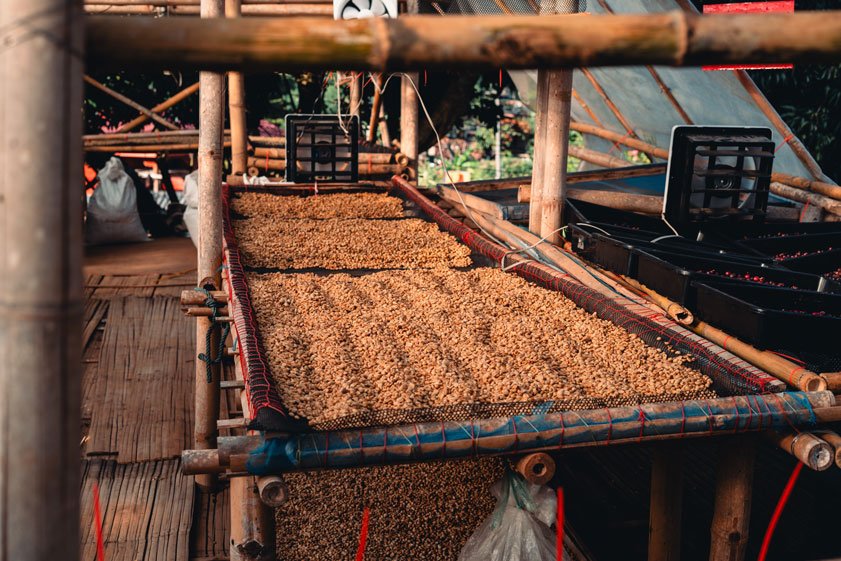

Sustainable coffee farming techniques include shade-grown methods, which can also be used during the drying process.
Implementing Agroforestry Systems for Carbon Sequestration
Agroforestry systems combine multiple crops or trees with coffee plants to create a diverse ecosystem. These systems not only sequester carbon dioxide but also promote biodiversity, reduce soil erosion, and provide habitat for beneficial insects and microorganisms. By adopting agroforestry practices, farmers can contribute to climate change mitigation while producing high-quality coffee.
Educating Farmers About Sustainable Agriculture Best Practices
Educating farmers about sustainable agriculture best practices is crucial for widespread adoption of sustainable coffee farming methods.
Workshops, training programs, and extension services can provide farmers with the necessary skills and knowledge to implement these practices.
Additionally, certification programs like Fairtrade, Organic, or Rainforest Alliance can incentivize farmers to adopt sustainable practices.
The Last Drop
The coffee industry faces numerous challenges that threaten its long-term sustainability. Climate change, pest infestations, soil degradation, and water scarcity are just a few of the issues affecting coffee production. However, by adopting sustainable farming practices, farmers can mitigate these risks and produce high-quality coffee while promoting environmental stewardship.
Sustainable coffee farming is not only good for the environment but also beneficial for farmers and consumers alike. By choosing certified sustainable coffee products, consumers can support farmers who prioritize environmental sustainability and social responsibility. As demand for sustainable coffee grows, it is essential that farmers, traders, and roasters work together to promote environmentally friendly practices throughout the supply chain.
The future of coffee production depends on our ability to adopt sustainable farming practices. By reducing chemical runoff, promoting biodiversity, and sequestering carbon dioxide, we can ensure a greener future for our planet. As consumers, it is our responsibility to demand high-quality, sustainably produced coffee that not only tastes great but also supports a more environmentally conscious industry.